| awk使用详解(三)变量、数字表达式、赋值运算符、BGGIN、END、Built | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › awk 例子 › awk使用详解(三)变量、数字表达式、赋值运算符、BGGIN、END、Built |
awk使用详解(三)变量、数字表达式、赋值运算符、BGGIN、END、Built
|
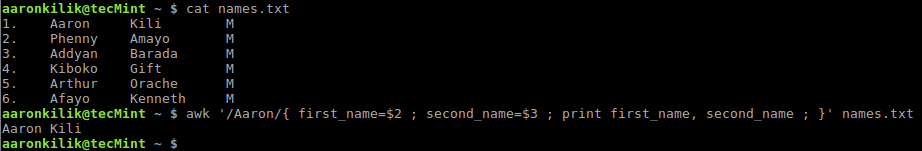
Awk 变量、数字表达式、赋值运算符1. Awk 变量:以下是定义Awk变量 variable_name=value 句法中: 1. variable_name: 是一个变量 2. value: 存储在变量中的值 例如: computer_name=”tecmint.com” port_no=”22” email=”[email protected]” server=”computer_name” 例如变量接收一个域 first_name=$2 second_name=$3 first_name is 设置为第二个域、 second_name is 设置成第三个域. names.txt 文件如下: $ cat names.txt
使用变量 first_name 和 second_name 来保存第一个用户的第一和第二个名字。以下是Awk例子: $ awk '/Aaron/{ first_name=$2 ; second_name=$3 ; print first_name, second_name ; }' names.txt
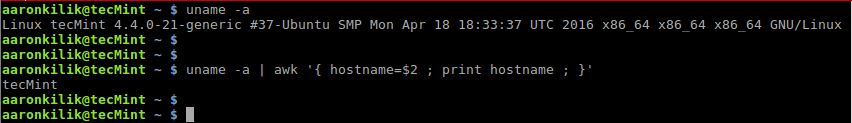
uname -a 打印系统信息. hostname, 我们能保存 hostname 在变量 hostname中,使用 Awk 打印出来: $ uname -a$ uname -a | awk '{hostname=$2 ; print hostname ; }'
I Awk中, 数字操作符: 1. * : 乘 2. + : 加 3. / : 除 4. - : 减肥 5. % : 余 6. ^ : 幂 数字表达式: $ operand1 operator operand2 counter=0 num1=5 num2=10 num3=num2-num1 counter=counter+1 以下为包含:域名的domains.txt 文件 news.tecmint.com tecmint.com linuxsay.com windows.tecmint.com tecmint.com news.tecmint.com tecmint.com linuxsay.com tecmint.com news.tecmint.com tecmint.com linuxsay.com windows.tecmint.com tecmint.com 查看文件: $ cat domains.txt
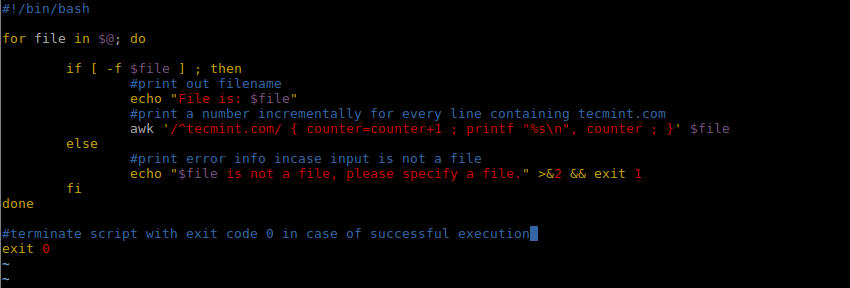
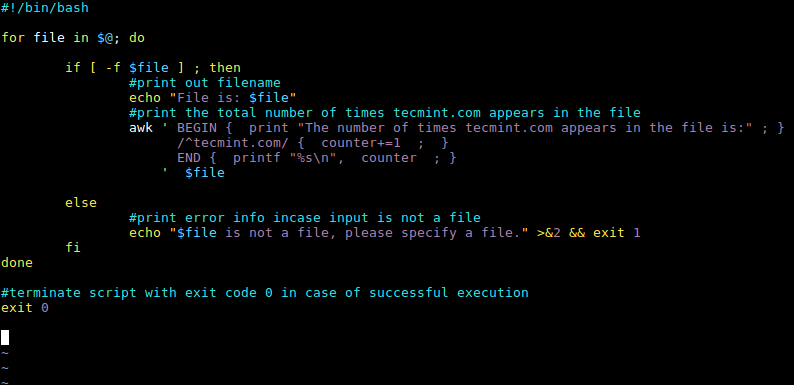
以下计算 tecmint.com 在文件中使用次数: #!/bin/bashfor file in $@; doif [ -f $file ] ; then#print out filenameecho "File is: $file"#print a number incrementally for every line containing tecmint.com awk '/^tecmint.com/ { counter=counter+1 ; printf "%s\n", counter ; }' $fileelse#print error info incase input is not a fileecho "$file is not a file, please specify a file." >&2 && exit 1fidone#terminate script with exit code 0 in case of successful execution exit 0
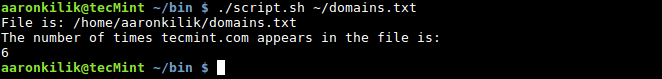
保存脚本,以下为运行脚本: $ ./script.sh ~/domains.txt
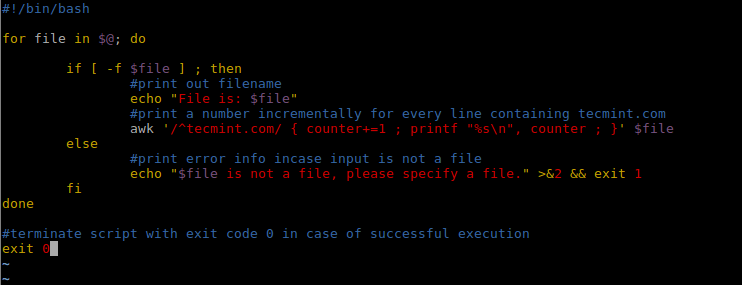
1. *= : multiplication assignment operator 2. += : addition assignment operator 3. /= : division assignment operator 4. -= : subtraction assignment operator 5. %= : modulus assignment operator 6. ^= : exponentiation assignment operator 句法: $ variable_name=variable_name operator operand 例子: counter=0 counter=counter+1 num=20 num=num-1 例子: variable_name operator=operand counter=0 counter+=1 num=20 num-=1 以下为使用: += 操作符的shell脚本: #!/bin/bashfor file in $@; doif [ -f $file ] ; then#print out filenameecho "File is: $file"#print a number incrementally for every line containing tecmint.com awk '/^tecmint.com/ { counter+=1 ; printf "%s\n", counter ; }' $fileelse#print error info incase input is not a fileecho "$file is not a file, please specify a file." >&2 && exit 1fidone#terminate script with exit code 0 in case of successful execution exit 0
句法: # awk 'script' filenames Awk 脚本 /pattern/ { actions } 使用 BEGIN 和 END. awk ' BEGIN { actions } /pattern/ { actions } /pattern/ { actions }………. END { actions } ' filenames 1. BEGIN 模式使用于脚本时, 在开始读入输入行之前,所有的动作被执行一次. 2. 输入行并解析. 3. 执行匹配的输入行动作. 4. 重复2、3步. 5. 当读完所有输入行, END 模式被执行. news.tecmint.com tecmint.com linuxsay.com windows.tecmint.com tecmint.com news.tecmint.com tecmint.com linuxsay.com tecmint.com news.tecmint.com tecmint.com linuxsay.com windows.tecmint.com tecmint.com $ cat ~/domains.txt
以下文本例子: #!/bin/bashfor file in $@; doif [ -f $file ] ; then#print out filenameecho "File is: $file"#print a number incrementally for every line containing tecmint.com awk '/^tecmint.com/ { counter+=1 ; printf "%s\n", counter ; }' $fileelse#print error info incase input is not a fileecho "$file is not a file, please specify a file." >&2 && exit 1fidone#terminate script with exit code 0 in case of successful execution exit 0以下是使用 BEGIN 和END awk '/^tecmint.com/ { counter+=1 ; printf "%s\n", counter ; }' $file To: awk ' BEGIN { print "The number of times tecmint.com appears in the file is:" ; }/^tecmint.com/ { counter+=1 ; }END { printf "%s\n", counter ; } ' $fileshell 脚本如下: #!/bin/bashfor file in $@; doif [ -f $file ] ; then#print out filenameecho "File is: $file"#print the total number of times tecmint.com appears in the fileawk ' BEGIN { print "The number of times tecmint.com appears in the file is:" ; }/^tecmint.com/ { counter+=1 ; }END { printf "%s\n", counter ; } ' $fileelse#print error info incase input is not a fileecho "$file is not a file, please specify a file." >&2 && exit 1fidone#terminate script with exit code 0 in case of successful execution exit 0
以上首先打印 domains.txt文件, 然后Awk 脚本被执行, BEGIN 模式输出“The number of times tecmint.com appears in the file is:” 。然后, /^tecmint.com/ 比较每一个输入行且动作在 { counter+=1 ; }时,被执行计数 tecmint.com 。最后 END 模式 打印出tecmint.com总的计数。 $ ./script.sh ~/domains.txt
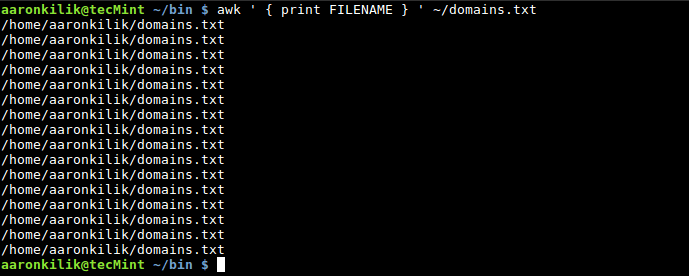
1. FILENAME : 输入文件名( 不改变量名) 2. FR : 输入行号 (1, 2, 3… 等, 不改变量名) 3. NF : 输入行域号 (不改变变量名) 4. OFS : 输出域分隔符 5. FS : 输入域分隔符 6. ORS : 输出记录分隔符 7. RS : 输入记录分隔符 例子: $ awk ' { print FILENAME } ' ~/domains.txt
Awk 缺省行为是使用 FILENAME built-in 变量. 使用 NR :注意空行 $ cat ~/domains.txt
$ awk ' END { print "Number of records in file is: ", NR } ' ~/domains.txt
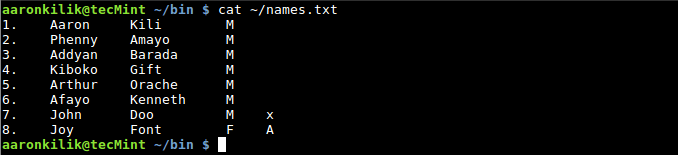
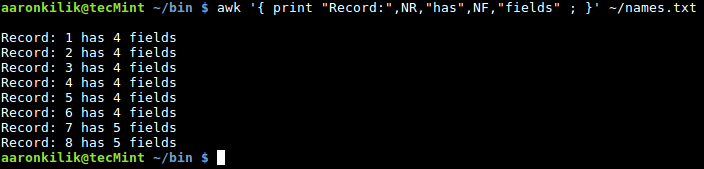
使用NR built-in 变量计数: $ cat ~/names.txt
$ awk '{ print "Record:",NR,"has",NF,"fields" ; }' ~/names.txt
使用 FS built-in变量,分割输入行到域. 缺省 FS 是 space 和tab, 有两个方法: 1. 方法一使用 FS built-in 变量. 2. 第二个方法使用 -F Awk选项 考虑到 /etc/passwd 是系统文件;使用,: 字符, 因此可以说明一个新的输入域名分隔符,过滤某些域。: 使用 -F 选项: $ awk -F':' '{ print $1, $4 ;}' /etc/passwd
使用 FS built-in 变量优化: $ awk ' BEGIN { FS=“:” ; } { print $1, $4 ; } ' /etc/passwd |
【本文地址】